How AC condenser works
An air conditioner is a vital appliance for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature. Have you ever wondered how does an air conditioner work step by step? The principle of air conditioning lies in the ability to remove hot air and replace it with cool air. The AC condenser plays a crucial role in this process.
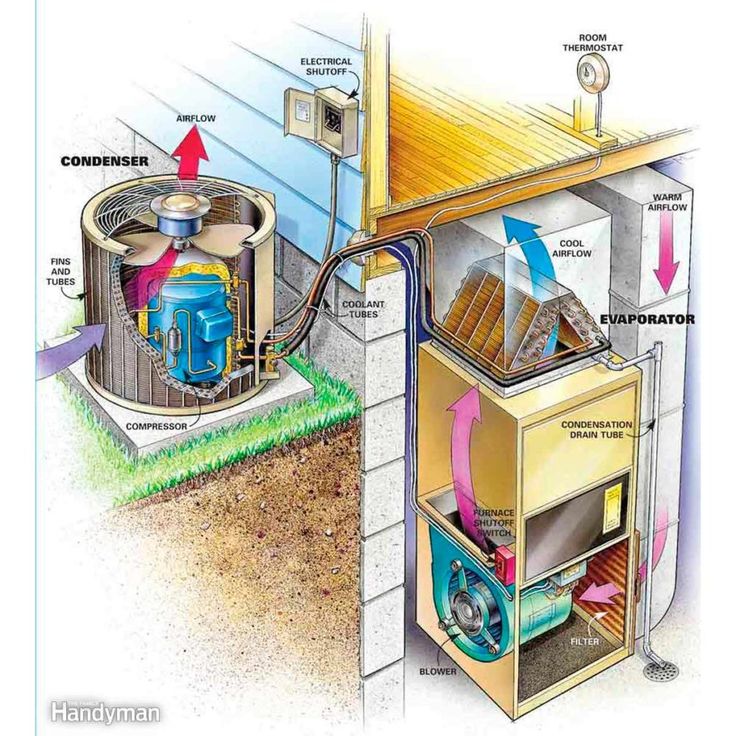
The air conditioner condenser is responsible for cooling down and condensing the refrigerant, allowing it to release heat accumulated from the indoor air. As the condenser receives the hot gas refrigerant, it goes through a series of stages, transforming it from a high-pressure vapor to a high-pressure liquid. This transition is essential for the proper functioning of the air conditioning system.
So, how does a AC condenser work exactly? The process begins with the high-pressure vapor refrigerant flowing into the condenser coils. These coils are designed to maximize the surface area for heat exchange. As the refrigerant passes through the coils, it releases heat to the surrounding air, cooling down and condensing in the process.
A diagram illustrating how an air conditioner works helps visualize the process. The refrigerant starts as a high-pressure vapor in the compressor, then enters the condenser as a hot gas. The condenser coils facilitate the heat transfer, transforming the refrigerant into a high-pressure liquid. From here, the refrigerant flows into the expansion valve, where it undergoes a pressure drop and evaporates, absorbing heat from the indoor air and cooling it down. Finally, the refrigerant returns to the compressor, starting the cycle again.
In conclusion, understanding how an air conditioner condenser works is crucial for comprehending the overall operation of an air conditioning system. The AC condenser plays a critical role in cooling down the refrigerant and releasing heat to the outdoor environment. By following each step of the process, from the high-pressure vapor to the high-pressure liquid, you can gain a deeper understanding of how an AC condenser works and its importance in maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature.“Hvac basic knowledge”
Understanding How an AC Condenser Works
The AC condenser, also known as the air conditioning condenser, plays an essential role in the cooling process of air conditioning systems. It is responsible for releasing heat from the refrigerant that has been absorbed from the indoor surroundings. By understanding how an AC condenser works, you can gain a better understanding of how your air conditioner functions.
The AC condenser works in conjunction with other components in the air conditioning system to cool and dehumidify the air. Here is a step-by-step guide on how an AC condenser works:
- Step 1: Compression and Condensation
- The process begins with the compression of the refrigerant gas by the compressor.
- This compression increases the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant.
- The high-pressure refrigerant then flows towards the AC condenser.
- As the refrigerant enters the condenser, it starts to lose heat and transition from a gas to a liquid state.
- Step 2: Heat Dissipation
- The condenser is designed with a series of metal fins and coils that maximize its surface area.
- As the refrigerant flows through the condenser, the fins and coils allow for efficient heat transfer.
- Heat from the refrigerant is dissipated into the surrounding air, lowering the temperature of the refrigerant.
- The cooled liquid refrigerant then continues its journey towards the expansion valve.
- Step 3: Expansion and Evaporation
- The liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, which reduces its pressure.
- This pressure drop causes the refrigerant to expand and evaporate into a gas.
- During this evaporation process, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling it down.
- The now-gaseous refrigerant then returns to the compressor to repeat the cycle.
This step-by-step process of how an AC condenser works is an essential part of the overall functioning of an air conditioning system. By releasing heat and facilitating the refrigerant’s transition from a gas to a liquid, the condenser ensures that the air conditioning system is able to cool and dehumidify the indoor air effectively.
Understanding how an AC condenser works can help you identify potential issues and perform basic maintenance to keep your air conditioning system running smoothly. Regularly cleaning the condenser fins and coils, checking for any obstructions, and ensuring proper airflow can help optimize the performance and efficiency of your AC condenser.
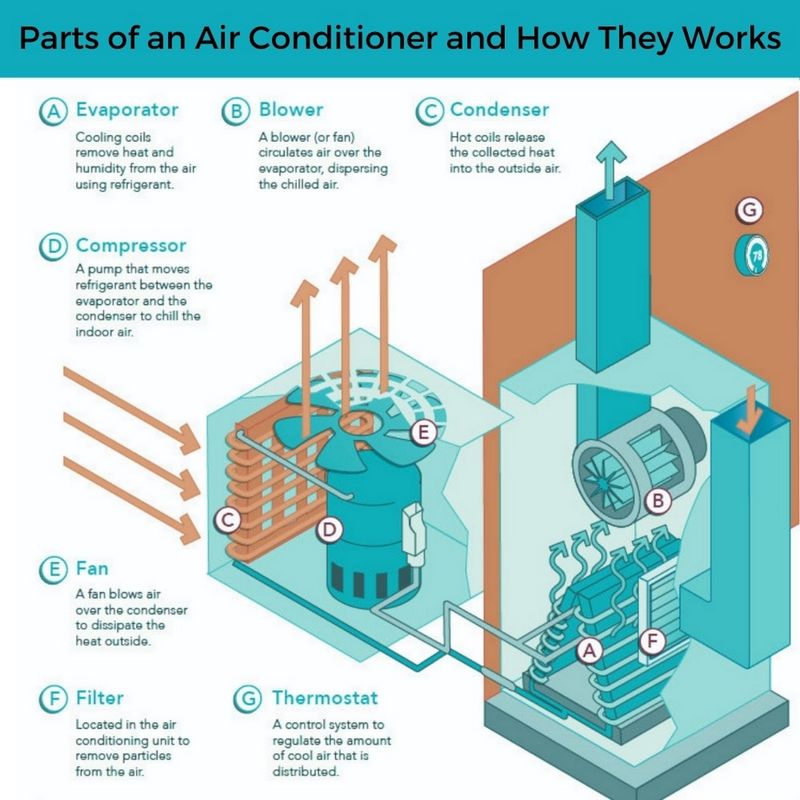
Basic Components
An air conditioner works by removing heat from the air inside your home and transferring it outside. To do this, it relies on several key components that work together to cool the air and circulate it throughout the space. Understanding these basic components is essential to understanding how an AC condenser works.
Here are the main components of an air conditioner:
- Compressor: The compressor is the heart of an air conditioning system. It pressurizes the refrigerant gas, raising its temperature and converting it into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
- Condenser Coil: The condenser coil is located in the outdoor unit of the air conditioner. It receives the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas from the compressor and cools it down, causing it to condense into a liquid state. As the refrigerant condenses, it releases heat to the surrounding environment.
- Condenser Fan: The condenser fan is responsible for drawing air across the condenser coil, helping to cool down the hot refrigerant as it flows through the coil. This fan is usually mounted on the outdoor unit and blows the hot air away from the condenser coil.
- Expansion Valve: The expansion valve is a small device located between the condenser coil and the evaporator coil. It acts as a restriction, allowing the high-pressure refrigerant liquid to expand and convert into a low-pressure, low-temperature liquid-vapor mixture.
- Evaporator Coil: The evaporator coil is located in the indoor unit of the air conditioner. It receives the low-pressure, low-temperature liquid-vapor mixture from the expansion valve. As the warm air from your home blows across the evaporator coil, the refrigerant inside the coil absorbs heat from the air and evaporates into a gas.
- Evaporator Fan: The evaporator fan, located in the indoor unit, circulates the air inside your home over the evaporator coil, facilitating the heat exchange process. This fan blows the cool air back into the room.
These components work together in a continuous cycle to cool your home. The compressor pressurizes and heats the refrigerant gas, the condenser coil cools and condenses the gas into a liquid, the expansion valve expands the liquid, and the evaporator coil absorbs heat from the air, cooling it down before the process begins again. This continuous cycle is what allows an air conditioner to cool the indoor air and maintain a comfortable temperature.
By understanding the basic components of an air conditioner and how they work together, you can better appreciate the principle of air conditioning and how an AC condenser plays a crucial role in the cooling process.
Step 1: Air Circulation
Before we understand how an AC condenser works, it is important to learn about the basic principle of air conditioning. Air conditioning systems work based on the principle of thermodynamics, which involves the transfer of heat. The main components of an air conditioning system include the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve.
The condenser is responsible for releasing the heat absorbed from the indoor air to the outdoor environment. This process is achieved through a series of steps, starting with the circulation of air.
When the air conditioning system is turned on, the indoor air is drawn into the evaporator coil. The evaporator coil contains a cold refrigerant that absorbs heat from the indoor air, resulting in cool air being blown back into the room. The refrigerant then becomes a gas and travels to the compressor.
The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, increasing its temperature and turning it back into a high-pressure gas. This hot gas is then sent to the condenser coil, which is located outside the house. The condenser coil is responsible for releasing the heat absorbed from the indoor air to the outdoor environment.
As the hot refrigerant gas flows through the condenser coil, a fan blows air over the coil, aiding in the heat transfer process. The heat from the refrigerant is transferred to the air, causing the refrigerant to condense into a high-pressure liquid.
The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure. This causes the refrigerant to evaporate and cool down rapidly. The cool refrigerant is then sent back to the evaporator coil, where it absorbs heat from the indoor air again, starting the cycle all over again.
So, in summary, the process of air circulation in an AC condenser involves the circulation of indoor air through the evaporator coil, which absorbs heat from the air. The heat is then transferred to the condenser coil, where it is released to the outdoor environment. This continuous cycle allows an air conditioning system to cool indoor spaces efficiently.
Step 2: Refrigerant Compression
Once the refrigerant has been evaporated and collected heat from the indoor air in the evaporator coil, it now enters the compressor, which is located in the outdoor unit of the air conditioner.
The compressor is essentially the heart of the air conditioning system. Its main function is to compress the low-pressure refrigerant gas, which is at a relatively low temperature, into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
This compression process is crucial because it helps increase the energy of the refrigerant, allowing it to release the absorbed heat more efficiently. The compressed refrigerant is then ready to move on to the next step of the cooling cycle.
In a typical air conditioning system, the compressor works by using a piston or a rotating vane to compress the refrigerant. As the refrigerant gas enters the compressor, it is compressed and its pressure is increased, causing its temperature to rise as well. This high-pressure, high-temperature gas is then expelled from the compressor and flows into the next component of the system.
The refrigerant compression process plays a vital role in the overall functioning of an air conditioner. It ensures that the refrigerant is at the right pressure and temperature to effectively release heat and provide cool air to the indoor space.
Key Points: Refrigerant Compression
| Key Point | Explanation |
| Refrigerant Compression | The process of compressing low-pressure refrigerant gas into high-pressure, high-temperature gas. |
| Important Function | Increases the energy of the refrigerant, allowing it to release absorbed heat more efficiently. |
| Compressor | The component responsible for compressing the refrigerant using a piston or rotating vane. |
| High-Pressure Gas | The result of compression, ready to move on to the next step of the cooling cycle. |
| Crucial Role | Ensures proper pressure and temperature for efficient heat release and cooling. |
Understanding how the refrigerant is compressed is an essential part of comprehending how an air conditioner works. By following the step-by-step process, from condensation to compression, you can gain a deeper understanding of the principle of air conditioning and appreciate the complex mechanisms involved.
Step 3: Condensation Process
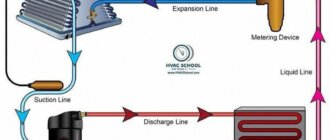
The condensation process is an essential part of the principle of air conditioning. It is responsible for transforming hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas into a cool, low-pressure liquid.
So, how does an air conditioner condenser work? Let’s break it down:
- Once the refrigerant leaves the compressor, it enters the condenser coil.
- The condenser coil is located in the outdoor unit of the air conditioner and is designed to dissipate heat.
- As the hot refrigerant gas flows through the condenser coil, it comes into contact with the cooler outside air.
- This contact causes the refrigerant to release heat, allowing it to cool down and transform into a liquid state.
- During this process, the condenser fan blows air over the condenser coil to facilitate the heat transfer.
- As the refrigerant gives off heat and cools down, it changes from a gas to a liquid.
- The liquid refrigerant then flows out of the condenser coil and enters the expansion valve or metering device, which controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil.
It is important to note that the condensation process occurs in the outdoor unit of the air conditioner, specifically in the condenser coil. This is where the heat from the refrigerant is transferred to the outside air, which helps cool down the refrigerant and ensures efficient operation of the air conditioning system.
By understanding how the condensation process works, you can have a better grasp of how your air conditioner functions and troubleshoot any potential issues that may arise.
Step 4: Heat Exchange
Once the refrigerant has been compressed and turned into a high-pressure gas, it moves to the condenser, where the process of heat exchange takes place.
The condenser is a vital component of an air conditioner, responsible for releasing the heat absorbed from the indoor air. It works by transferring the heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding environment and converting it into a liquid form.
The condenser unit usually consists of a network of tubes and fins, which are designed to maximize the surface area for heat exchange. These tubes are typically made of copper or aluminum, which are excellent conductors of heat.
The hot refrigerant gas enters the condenser from the compressor and flows through the tubes. As the refrigerant flows through the condenser tubes, the cool air from the outside is blown across the fins using a fan or by the natural action of the wind.
As the cool air passes over the condenser fins, it absorbs the heat from the refrigerant, causing it to cool down and condense into a liquid state. This heat exchange process releases the heat absorbed from the indoor air and dissipates it into the surrounding atmosphere.
The condenser also plays a role in removing any latent heat from the refrigerant by condensing it into a liquid form. This step is crucial as it allows the refrigerant to cool down effectively and prepares it for the next stage of the air conditioning cycle.
Overall, the condenser’s role in the air conditioning system is to release the heat absorbed from the indoor air and prepare the refrigerant for the next cycle. Without a functioning condenser, the air conditioner would not be able to cool the indoor air effectively.
Step 5: Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is an important component of the air conditioning system. It is responsible for regulating the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil, which is located inside the air conditioner.
So how does an AC condenser work with the expansion valve? Let’s break it down:
- Refrigerant enters the expansion valve: Once the refrigerant leaves the compressor, it enters the expansion valve. This valve controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil by opening and closing.
- Pressure drop and cooling: As the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, there is a sudden drop in pressure. This decrease in pressure causes the refrigerant to cool down significantly.
- Evaporator coil and heat absorption: The cooled refrigerant then flows into the evaporator coil, where it absorbs heat from the indoor air. As the warm air passes over the coil, the refrigerant evaporates, removing heat from the air and cooling it down.
- Condensation and heat release: After the refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air, it becomes a high-pressure, high-temperature gas. This hot gas is then sent back to the condenser coil for the next stage of the cooling process.
The expansion valve plays a crucial role in maintaining the proper flow and pressure of the refrigerant throughout the air conditioning system. By regulating the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil, it helps ensure efficient cooling and proper temperature control.
In summary, the expansion valve is responsible for controlling the flow of refrigerant and regulating the pressure within the air conditioning system. It is a vital component in the process of transferring heat from indoors to outdoors, contributing to the overall function of the AC condenser.
Step 6: Evaporation
In the previous steps, we learned about the processes of compression and condensation in an air conditioning system. Now, let’s move on to the next step, which is evaporation.
Evaporation is an essential part of the cooling process in an air conditioner. It takes place in the evaporator coil, which is located in the indoor unit of the system. The evaporator coil contains a refrigerant that has been previously condensed and is now in a low-pressure, low-temperature state.
When the indoor air is blown over the evaporator coil, the refrigerant inside the coil absorbs the heat from the air. As a result, the temperature of the refrigerant rises, and it changes from a liquid state to a gaseous state. This phase change from liquid to gas is known as evaporation.
During evaporation, the refrigerant absorbs a significant amount of heat from the indoor air, which makes the air cooler. Thus, the evaporator coil acts as a heat exchanger, cooling the air that is circulated throughout your home or office.
To promote efficient evaporation, the evaporator coil is designed with a large surface area. This helps to maximize the contact between the refrigerant and the air, allowing for better heat transfer. Additionally, the coil is usually made of metal with good thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum, to enhance the heat transfer process.
Once the refrigerant has evaporated and absorbed the heat from the indoor air, it enters the compressor for the next stage of the cooling cycle – compression.
In summary, evaporation is the process by which the refrigerant in the evaporator coil changes from a liquid to a gas, absorbing heat from the indoor air and cooling it down. This is a vital step in the air conditioning cycle that helps to maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
Step 7: Repeat Cooling Cycle
Once the warm air is pushed out of the condenser coil and the heat is transferred to the outdoor air, the cooling cycle needs to be repeated in order to continue lowering the temperature inside your home or office. The air conditioner condenser works in a continuous cycle to maintain a comfortable temperature indoors.
To understand how the process is repeated, let’s recap the principle of air conditioning:
- The air conditioner takes in warm air from the indoor environment and passes it over evaporator coils.
- The refrigerant inside the evaporator coils absorbs the heat from the warm air and evaporates into a gas.
- The compressor then pressurizes the gas, increasing its temperature and pressure.
- Next, the hot refrigerant gas is released into the condenser coil, which is located outside the building.
- The condenser coil’s fan blows outdoor air over the coil, causing the refrigerant gas to release its heat and condense back into a liquid state.
- The liquid refrigerant then travels back to the evaporator coils, where the process starts again.
So, in the repeat cooling cycle, the air conditioner continues to draw in warm air from the indoor environment, extract the heat from it through evaporation, and release that heat to the outdoor air via the condenser coil. This continuous process keeps the indoor temperature cool and comfortable.
It’s important to note that the air conditioning system does require periodic maintenance and cleaning to ensure optimal performance. Regularly cleaning the condenser coils, changing air filters, and checking refrigerant levels are vital to keep the system running efficiently.
Common Issues
While the AC condenser is a crucial component of an air conditioning system, it can experience various issues that can impact its performance. Here are some common issues that you may encounter with an AC condenser:
- Clogged or Dirty Coils: Over time, dust, dirt, and debris can accumulate on the condenser coils, restricting airflow and reducing the efficiency of the condenser. Regular cleaning and maintenance can help prevent this issue.
- Refrigerant Leaks: The condenser contains refrigerant that helps cool the air. If there is a leak in the condenser, the refrigerant levels can drop, leading to reduced cooling capacity. A professional technician should be called to locate and repair any refrigerant leaks.
- Electrical Problems: The condenser relies on electrical connections and components to function properly. Faulty wiring or electrical components can cause the condenser to malfunction or fail altogether. It is important to have a qualified technician inspect and repair any electrical problems.
- Fan Issues: The condenser relies on a fan to remove heat from the coils. If the fan becomes damaged or stops working, it can lead to poor heat dissipation and affect the overall cooling capacity. Regular maintenance and inspection can help identify and address any fan issues.
- Overheating: If the condenser becomes overheated, it can result in a shutdown of the entire air conditioning system. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as limited airflow, refrigerant issues, or electrical problems. Regular maintenance and cleaning can help prevent overheating.
It is important to address these common issues promptly to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your AC condenser. Regular maintenance and inspections by a qualified technician can help identify and resolve any potential problems before they escalate.
Maintenance Tips
To ensure your AC condenser operates efficiently and maintains its performance, it is essential to perform regular maintenance. Here are some maintenance tips to keep your AC condenser working optimally:
- Clean the Condenser Filters: The condenser filters can collect dirt, dust, and debris over time, obstructing airflow. Regularly cleaning or replacing the filters can enhance the efficiency of your AC condenser.
- Inspect the Coils: The condenser coils are responsible for transferring heat. Regularly inspect the coils for any dirt or debris buildup and clean them if necessary.
- Check for Refrigerant Leaks: Low refrigerant levels can impact the performance of your AC condenser. Monitor the refrigerant levels regularly and repair any leaks promptly.
- Clean the Surrounding Area: Ensure that the area around the AC condenser is clear of any debris, vegetation, or obstructions. This allows for adequate airflow and prevents overheating.
- Inspect Electrical Connections: Check the electrical connections of your AC condenser for any loose or damaged wires and connections. Faulty electrical connections can affect the functioning of the unit.
- Schedule Regular Professional Maintenance: It is recommended to have your AC condenser serviced by a professional at least once a year. They can inspect and address any potential issues and ensure optimal performance.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the lifespan of your AC condenser and enjoy efficient cooling throughout the warm months.
Energy Efficiency
In addition to cooling your home, it is important to consider the energy efficiency of your AC condenser. Energy efficiency refers to the amount of energy required to produce a certain level of cooling. A more energy-efficient condenser will use less electricity and result in lower energy costs for the homeowner.
There are several factors that contribute to the energy efficiency of an AC condenser:
- Size: The size of the AC condenser should be properly matched to the size of the home. An oversized condenser will cycle on and off frequently, wasting energy. On the other hand, an undersized condenser may struggle to cool the space effectively.
- SEER Rating: The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) measures the efficiency of an air conditioner. A higher SEER rating indicates a more energy-efficient unit. Look for condensers with a SEER rating of at least 14 for optimal energy efficiency.
- Coil Design: The coil design of the condenser affects its efficiency. A coil with more surface area allows for better heat transfer and more efficient cooling.
- Refrigerant: The type of refrigerant used in the condenser can impact energy efficiency. Older units may still use R-22 refrigerant, which is being phased out due to its harmful impact on the environment. Newer units use R-410A, which is more environmentally friendly and energy efficient.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the condenser coils and replacing air filters, can help keep the unit running efficiently. A clean condenser and unrestricted airflow ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
By choosing an energy-efficient AC condenser and properly maintaining it, you can not only save money on your energy bills but also reduce your carbon footprint. Understanding the principles of air conditioning and how the condenser component works is essential in making informed decisions about energy efficiency.
Choosing the Right Condenser
When it comes to selecting the right condenser for your air conditioning system, there are several factors that need to be considered. The condenser plays a crucial role in the cooling process of an air conditioner, as it helps to dissipate the heat that is absorbed by the evaporator coil.
Here are some important points to keep in mind when choosing the right condenser:
- Size: The size of the condenser unit should be matched to the cooling capacity of your air conditioner. It is important to ensure that the condenser is not too large or too small for your specific needs. An oversized condenser can lead to short cycling and energy inefficiency, while an undersized condenser may not effectively cool your space.
- Efficiency: Consider the energy efficiency rating of the condenser. Look for a high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating, as this indicates better energy efficiency and lower operating costs. Higher SEER ratings also mean greater environmental friendliness.
- Noise Level: Take into account the noise level of the condenser. Some condensers are designed with noise-reducing features, such as sound-dampening technology or quieter fan systems. If noise is a concern for you, look for a condenser with a low decibel rating.
- Reliability: Consider the reliability and durability of the condenser. Look for a condenser made from high-quality materials and backed by a reliable manufacturer warranty. A reliable condenser will ensure a long lifespan and minimize the risk of breakdowns and repairs.
- Installation Requirements: Determine the specific installation requirements for the condenser. Consider factors such as space availability, access for maintenance, and local building codes. Consult with a professional HVAC technician to ensure proper installation.
In summary, choosing the right condenser for your air conditioning system is crucial for optimal performance and energy efficiency. Consider the size, efficiency, noise level, reliability, and installation requirements when making your decision. Consulting with a professional HVAC technician can provide additional guidance and help ensure that you select the right condenser for your specific needs.
Q&A:
What is an AC condenser and how does it work?
An AC condenser is a key component in an air conditioning system that is responsible for cooling the refrigerant. It works by compressing the refrigerant gas, causing it to become a high-pressure, high-temperature vapor. This vapor then flows through a series of coils where it releases heat and becomes a liquid. The condenser fan then blows air over the coils, cooling the refrigerant and releasing the heat outside.
What are the main components of an AC condenser?
The main components of an AC condenser include the compressor, condenser coils, condenser fan, refrigerant, and various valves and sensors. The compressor is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas, while the condenser coils provide a large surface area for heat exchange. The condenser fan blows air over the coils, and the refrigerant acts as a medium for heat transfer. Valves and sensors help regulate the flow and temperature of the refrigerant.
What are some common problems with AC condensers?
Some common problems with AC condensers include refrigerant leaks, faulty compressors, clogged condenser coils, and issues with the condenser fan. Refrigerant leaks can lead to reduced cooling capacity and increased energy consumption. A faulty compressor may result in inadequate pressure and temperature control. Clogged condenser coils can hinder heat exchange, while issues with the condenser fan can lead to inadequate airflow and inefficient cooling.
How often should an AC condenser be maintained?
An AC condenser should be maintained at least once a year to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Regular maintenance tasks include cleaning the condenser coils, checking for refrigerant leaks, lubricating moving parts, and inspecting electrical connections. Additionally, it is important to change the air filters regularly to prevent debris from clogging the condenser coils and reducing airflow.